Table of Contents
- Mobile Operating System Market Share
- Why Is Android More Popular Globally While iOS Dominates The US?
- Hardware And Software Differences
- Demographics And Behavior
- When Choosing A Platform For Your Mobile App
- Target Market And Demographic
- Comparison Chart: iOS Vs Android
- Understanding The Differences: iphone Vs Android Users
Smartphones are constantly evolving, with new models released by both Apple and Android brands. While consumers and experts debate the pros and cons of each platform, businesses must consider the differences in features, pricing, technical specs, and performance when building a mobile app. Additionally, it’s essential to understand the distinct user personas of iPhone And Android Users. This guide will explore the key differences between iPhone And Android Users regarding demographics and behaviour. Understanding these differences can help businesses make informed decisions when choosing a platform for mobile app development. This information will benefit decision-makers in companies looking to improve their mobile development strategies.
Mobile Operating System Market Share
Android Vs iOS
Android and iOS have a duopoly over the global mobile operating system market, with Android accounting for about 70% market share and iOS at around 28% (as of August 2022). The percentage of iPhone users vs Android users in Europe (as of 2021) is similar at 32.1% and 67.2%, respectively.
Google Play offers around 3.55 million apps to Android users, making it the app store with the most available mobile apps (as of Q3 2022). iOS users can choose from about 1.6 million apps in the Apple App Store.
However, while Android prevails in the number of users and apps, iOS is ahead regarding mobile app revenue globally. Figures from market intelligence firm SensorTower indicate that consumer spending on apps from the Apple App Store reached $85.1 billion in 2021, while spending in the Google Play Store amounted to $47.9 billion.
Why Is Android More Popular Globally While iOS Dominates The US?
By the second quarter of 2022, iPhones overtook Android-powered devices in the hands of US consumers for the first time since Apple launched their smartphone in 2007 (according to a report from Counterpoint Research). Apple has now passed 50% market share (dubbed as “active installed base”) of US smartphones. The report notes that there had already been a strong trend of Android users in the United States shifting to iOS in the last four years.
There are a few common reasons that analysts often cite as to why Americans generally prefer the iPhone over Android devices. Some say it’s because Apple is an American company, and its devices (not just the iPhone) have long been staples in American popular culture. Some experts also say that US consumers have been more receptive to claims that the iPhone and the iOS ecosystem are superior regarding security and protecting user privacy.
Analysts point out that US consumers are generally less price sensitive on the economic front than those in many other countries. Apple is the least depreciating smartphone brand, making it the preferred choice for future trade-ins and hand-me-downs.
Ultimately, Apple commands the highest satisfaction and loyalty ratings in the US among major smartphone brands (leading Samsung, Google, Motorola, and LG), albeit only with a razor-thin margin (according to a 2022 Statista Global Consumer Survey).
Hardware And Software Differences

iphone Vs Android
Before discussing the differences between iPhone And Android Users, one must understand the critical distinctions between the hardware and software they use.
Hardware Differences
Android users have a wide variety of devices to choose from, with options in screen sizes, processors, device features, and price points. In contrast, iPhone users are limited to Apple’s iPhone lineup. One notable difference is that Android phones typically have physical buttons for navigation, while iPhones have a touch-based navigational interface. This can be a matter of preference, but the physical buttons on Android phones can sometimes be more convenient.
Software Differences
In terms of the user interface, Android users have more customization options than iPhone users. They can reorganize their widgets and apps in many ways, whereas iPhone users are limited to a more simplistic grid layout. Additionally, the App Store has a stricter approval process resulting in fewer buggy or low-quality apps. However, this also means it can take longer for new apps to be approved and made available for Apple devices.
Demographics And Behavior
iPhone vs Android Users
Admittedly, it’s difficult to say whether one consumer segment is more likely to be an iPhone user or an Android user, as these things vary by country, change over time, and depend on many other variables. However, based on recent publicly available global data, here are some key takeaways on the differences between Android and iPhone users:
Income And Spending
iPhone users generally earn more than Android users – iPhones tend to attract premium or higher-income customers. In a 2018 survey (from US-based eCommerce platform Slickdeals), iPhone users reported an average annual income of $53,231 and $37,040 for Android users. The same study also said that iPhone users spend more on clothes, beauty products, and technology-related items than Android users.
Premium And Ultra-Premium Segment
Premium and ultra-premium consumers prefer the iPhone – Relatedly, Apple leads the market in the premium smartphone segment (according to a 2022 Counterpoint report), defined as smartphones with a wholesale price of at least $400, with 57% global market share. Furthermore, iPhones dominate the ultra-premium segment of $1,000+ devices with a 78% market share.
Age Group
Younger users prefer the iPhone, older generations prefer Android – In a 2019 survey (from the Mobile Ecosystem Forum), the percentage of iPhone users (44%) only outnumbered Android users (30%) in the 16-24-year-old age group. Android users lead iPhone users in older age groups. This appears to sync with US demographics, as iPhones show among 18-34-year-olds with a 58% share compared to 42% for Android (based on a 2019 report from Mercator Advisory Group). Conversely, older generations of US consumers prefer Android devices over the iPhone.
Customer Loyalty
Customer loyalty to both platforms is high and steady – Android users are more loyal than iOS users, albeit only slightly. Android has a 91% customer retention rate, compared to 86% for iOS (according to a 2018 report from Consumer Intelligence Research Partners).
Reasons For Switching
Reasons for switching from one OS to the other – Among the list of reasons, users switch from iOS to Android and vice versa in search of a better user experience, better features, and better pricing (according to a 2018 survey of US consumers from PCMag). 47% of those who switched from Android to iOS said that the latter provided a better UX, while only 30% stated that the change from iOS to Android delivered a better experience.
Security And Privacy
Apple users feel more secure than Android users – It’s difficult to definitively state that iOS is better at protecting user security and privacy than Android. While that may be the consensus among many security experts, they also say it’s not that simple. However, when it comes to perceptions, a 2022 survey found that consumers feel more secure using Apple devices than Android ones. In addition, among those surveyed who experienced security breaches, 75% of iOS users said they could fully recover their data compared to only 55% of Android users.
Push Notifications
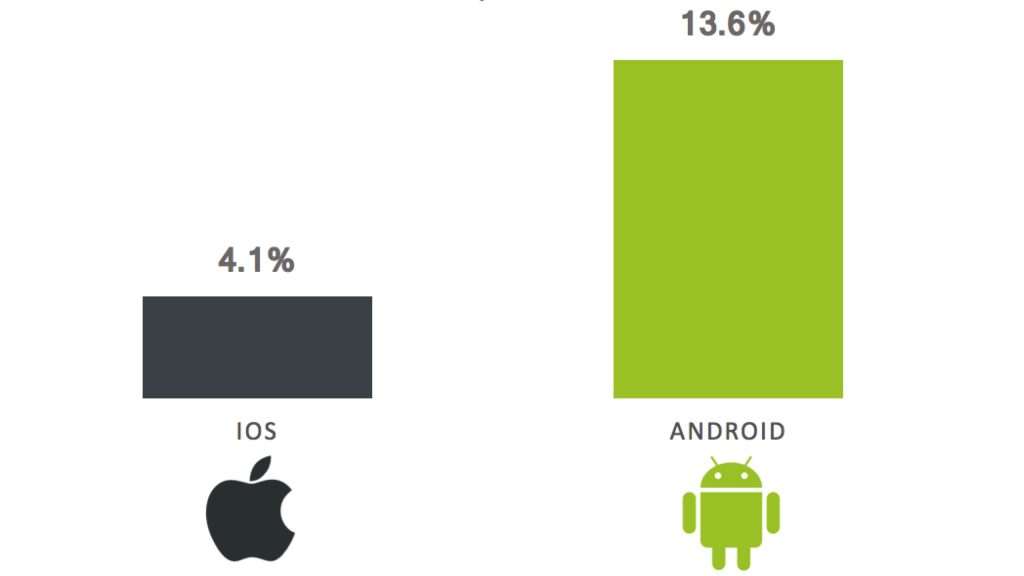
Android users are more responsive to push notifications. Android apps tend to perform better than iOS apps regarding user engagement from push notifications (based on a 2021 report from Airship). The reaction rate for Android is 4.6% versus 3.4% for iOS. Android users click more often on their push notifications than iPhone users. Android users also have a higher opt-in rate of 81% compared to their iOS counterparts at 51%. This means that more Android users choose to opt-in or receive push notifications. A key factor for this may be the ability for Android users to customize their notification settings, while iPhone users have less control over when and how notifications are received.
In conclusion, while there is no clear-cut answer as to whether one consumer segment is more likely to be an iPhone or Android user, these demographics and behaviour differences are worth considering when developing mobile apps or marketing strategies. Businesses should also remember that these differences may vary depending on the country and region and may change over time. It is essential to stay updated on current market trends and consumer preferences to target and engage with iPhone And Android Users effectively.
Aspects To Consider When Choosing A Platform For Your Mobile App
These facts demonstrate that the differences between iOS and Android users can impact a firm’s digital strategy. Hence, choosing a platform for a mobile application is a decision that should be considered. It’s common for businesses that want to be present on both platforms to launch on one first, then learn and improve the product before developing on the other. Companies must also decide whether to develop natively or through a cross-platform approach.
Target Market And Demographic
- Target market and demographic – If the app is intended for users outside of the United States and other high-income economies where the iPhone leads the market (e.g. UK, Canada, Japan), developing it first on Android is likely to be the optimal decision. Conversely, if the app is predominantly aimed at markets where the iPhone has a more substantial presence than Android devices, going for iOS is the preferable option. However, businesses must investigate this further within each market and drill down into customer segments. As the figures mentioned above indicate, higher-income individuals tend to prefer iPhones. It’s essential to do the research ahead on the preferred platform of specific audiences.
- Hardware options for consumers – iOS is only available on Apple devices, which are priced at a comparative premium. On the other hand, a wide range of consumer electronic brands (e.g. Samsung, Google, Motorola, LG, ASUS) use Android’s open-source operating system on their own smartphones. There are budget-friendly Android smartphones that cost as little as $150 and premium-range Android models.
- App development considerations (technologies, cost, duration, etc.) – Technology managers know that there are many variables during the development phase. The technology options obviously vary when weighing the implications of choosing between (or both) Android and iOS. When it comes to programming languages, businesses need talent in Java, C, C++, and Kotlin when developing for Android, while iOS developers use Objective-C or Swift. Access to (or availability of) developers isn’t necessarily a deterrent due to the vast talent pool of engineers globally for both platforms. Market rates differ, but iOS developers command slightly higher pay than those for Android (at least in the US). Of course, companies can significantly benefit from engaging in a mobile app development consultancy. When it comes to project duration, it ultimately depends on the requirements. Based on experience, the difference in project timelines between iOS and Android projects doesn’t vary significantly. Businesses also should consider cross-platform development approaches, which have proven to cut costs, speed up delivery, and simplify overall development. Even if a company already has an existing app on one platform (e.g. Android), cross-platform technologies (such as Kotlin Multiplatform) make it easier to expand to other platforms while continuously enhancing the existing app.
In summary, when choosing a platform for your mobile app, it is essential to consider the target market and demographic, the hardware options available for consumers, and the app development considerations such as technologies, cost, and duration. By carefully evaluating these factors, businesses can make a more informed decision on which platform to develop their app and ultimately create a more effective and successful mobile app.
Comparison Chart: iOS Vs Android
Feature | iOS | Android |
Developer | Apple | Open Handset Alliance and Google |
Hardware options | Apple (not available for other smartphone brands) | Samsung, Google, Motorola, LG, and ASUS, among others |
Programming language | Swift & Objective C | Java or Kotlin |
Source model | Proprietary (with some open-source elements) | Open source |
Language support | 40 languages | 100+ languages |
Marketplace for mobile apps | Apple App Store (no other app marketplaces allowed) | Google Play Store (plus other less popular marketplaces such as Aptoide and Galaxy Apps) |
Customizability | Limited | Highly customizable |
Global market share (percentage of users) | 28% | 70% |
Number of apps | 1.6 million | 3.55 million |
Global revenue of apps | $85.1 billion | $47.9 billion |
Age group | Preferred by younger users (18-34 years old) | Preferred by older users |
Economic profile | Higher income on average | Lower income on average |
Customer loyalty | High and steady (but slightly lower than Android) | High and steady (with a slight edge over iOS) |
In-app spending | More spent in mobile apps | Less spent in mobile apps |
User response to push notifications | Less responsive with a reaction rate of 3.4% and opt-in rate of 51% | More responsive with a reaction rate of 4.6% and opt-in rate of 81% |
User perception of security | Perceived as more secure | Perceived as less secure |
Compensation for developers (limited to US) | iOS developers are paid slightly more | Android developers are paid slightly less |
Understanding The Differences: iphone Vs Android Users
When developing a mobile app, it’s essential to understand the key differences between iPhone And Android Users regarding demographics, behaviour, and preferences. This knowledge can help businesses tailor their products to meet their target markets’ needs better and stay ahead of the competition. While resource constraints and testing product ideas may lead some companies to focus on only one platform, cross-platform technologies now make it easier to develop for multiple platforms, allowing companies to minimize the effort, cost, and risk of being present on both iOS and Android. Instead, they can focus on improving product features, engaging customers, and building the business.







